Case Report
Minimal Invasive Concept for the Rehabilitation of Edentulous Jaw with One-piece Implants
Jimoh Olubanwo Agbaje1 and Henri Diederich2*
1OMFS-IMPATH Research Group, Department of Imaging and Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Catholic University Leuven, Belgium
2Dental Clinic Henri Diederich, 51 av Pasteur, L- 2311 Luxembourg
*Address for Correspondence: Henri Diederich, Dental Clinic Henri Diederich, 51 av Pasteur, L- 2311 Luxembourg, Tel: +352-621-144-664; E mail: hdidi@pt.lu
Dates: 15 February 2018; Approved: 20 June 2018; Published: 21 June 2018
Citation this article: Agbaje JO, Diederich H. Minimal Invasive Concept for the Rehabilitation of Edentulous Jaw with One-piece Implants. Int J Case Rep Short Rev. 2018;4(2): 027-030.
Copyright: © 2018 Diederich H, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Keywords: One piece implants; Flapless surgery; Minimal invasive technique; Edentulous patient; Rehabilitation
Abstract
Background: One-piece implants encourage the use of minimally invasive surgical techniques in restoring edentulous spaces with minimal postoperative discomfort and excellent implant survival rate.
Case report: The compressive one piece implant can be used for multiple unit restorations with immediate loading in the upper and lower jaws. It can also be used in combination with a conventional implant and it can be placed flapless.
Conclusion: The presented case reports show the functional restoration of an edentulous patient with minimal invasive surgical technique with one piece implant in elderly patients.
Introduction
The use of conventional implants in the rehabilitation of edentulous space has been discussed extensively in the literature [1-4]. However, conventional implant systems may be limited or inapplicable in restoring some edentulous spaces due to various anatomical reasons. One of such reason is insufficient space between adjacent edentulous teeth for the use of a conventional implant e.g. regular Platform implants (3.5 - 4.5 mm diameter) or Wide Diameter implants (usually > 4.5 mm in diameter) which makes implant placement impossible [5-7,8,4]. In these situations, an alternative implant system for the restoration of such cases is required.
The One-piece implants help in restoring edentulous spaces that previously cannot be restored with conventional implants; it also encourages the use of minimally invasive surgical techniques which encourage maximum tissue preservation [9,10]. One-Piece implant offers a unique monobloc design that integrates both implant and superstructure, for a quick, simple one-stage procedure. Implants are specifically engineered for use in narrow ridges and tight spaces [11]. They are time effective as they eliminate the need for second stage surgery, mucosal healing period, and decrease patient exposure to additional pain and discomfort. The innovative geometries and advanced surface morphology of the implant offer high initial stability [12,13]. Single piece Implants are less invasive and can be immediately loaded in case of good bone quality, or progressively loaded in case of less than ideal bone quality.
One piece implant provides simple treatment sequence at lower cost and it offers the possibility to treat the elderly with minimal invasive implant placement (Flapless implant surgery) technique.
Flapless implant placement technique otherwise called minimally invasive procedure can be performed free hand, by using guided surgery or custom fabricated surgical guides made of casts taken at the first patient visit. This procedure, when applicable, provide patients and doctors with another treatment approach. Several clinical papers reported excellent short- and long-term survival rates (of about 98.7% at 2 years) for implants placed using flapless or minimally invasive approaches with the option of delivering immediately a pre-fabricated temporary prosthesis.
In term of implant prosthodontics, technical complexity is minimized with One-piece implants by reducing the number of components required, which also means that less treatment time is required. Patients benefit from having implants placed flapless and loaded immediately.
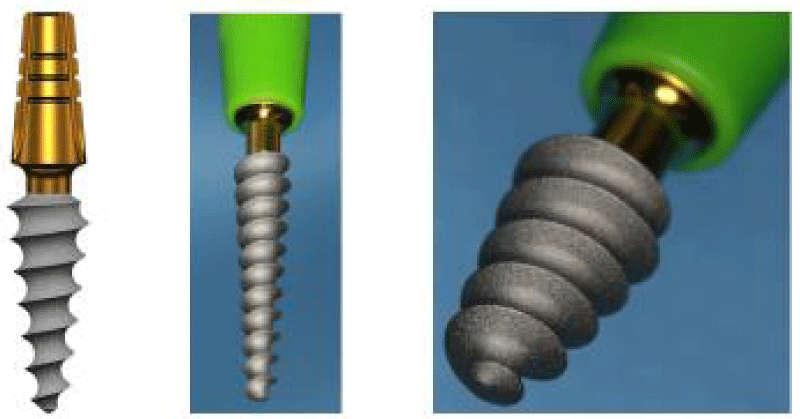
One piece implants (Figure 1) are machined in grade 23 titanium with an hydroxyapatite/beta tricalcium phosphate surface (HA/BTCP), the implant can be used to create single restorations in situations where high primary stability is achieved on placement.
The axial implants are generally intended for the anterior part of the mandible or the maxilla where there is sufficient bone height. They allow bicortical or even tricortical anchorage and provide good stability, even in medium-dense bone.
The following case reports describe procedures where one piece implants were used to rehabilitate edentulous jaws.
Case Presentations
Patient 1 is a 74-year-old lady, with removable prosthesis in the lower jaw who presented at the clinic with a reason to get fixed teeth in the mandible. A clinical examination showed an upper arch with few teeth and an edentulous lower arch with a resorbed ridge. Radiographic examination using an orthopantomogram showed an edentulous lower jaw with moderate vertical bone resorption in the front and severe vertical resorption in the premolar and molar region.
In the upper jaw, several teeth were present in the frontal region and in the lateral regions. Most of the teeth show a moderate bone loss suggestive of chronic periodontitis. Figure 2 shows the panoramic radiograph of the patient at presentation.
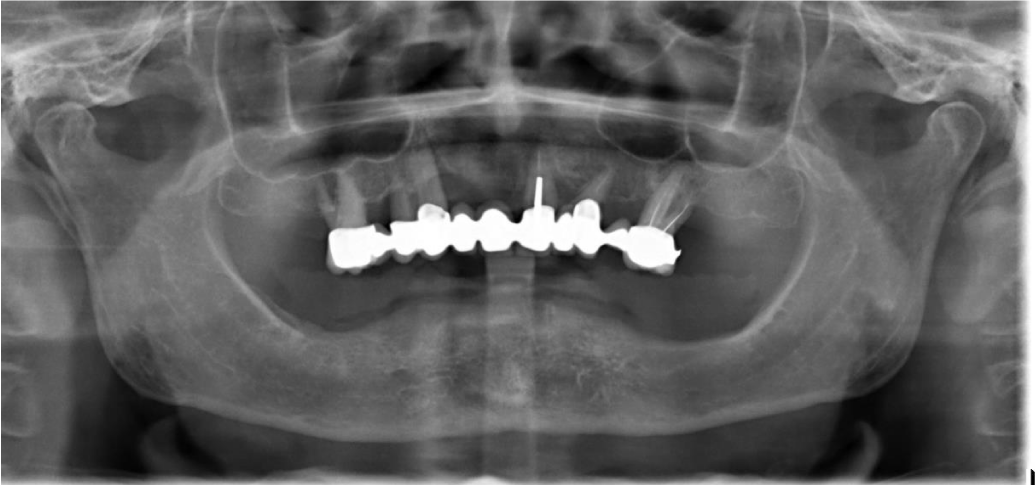 Figure 2: Panoramic radiograph of patient at presentation showing edentulous lower arch with resorbed alveolus and remaining upper teeth.
Figure 2: Panoramic radiograph of patient at presentation showing edentulous lower arch with resorbed alveolus and remaining upper teeth.
Treatment Plan: In the lower jaw sufficient one-piece implant with a compression thread (ROOTT implant system) will be provided to place a fixed bridge. The patient agreed to this treatment plan.
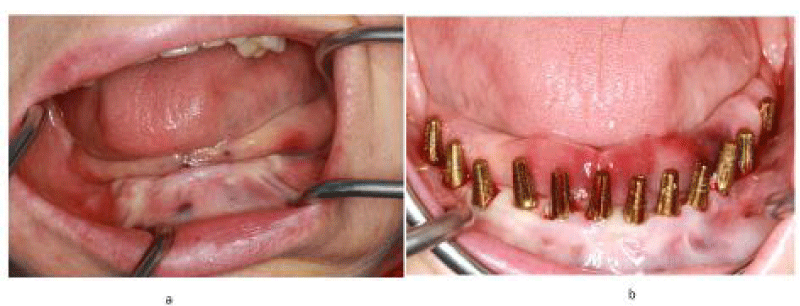
In the mandible, a minimal invasive technique was adopted. One-piece implants (length 8mm and diameter 4mm) were inserted one each in the region of 33 to 36 and the region of 43 to 46 with a minimum torque of 50N.
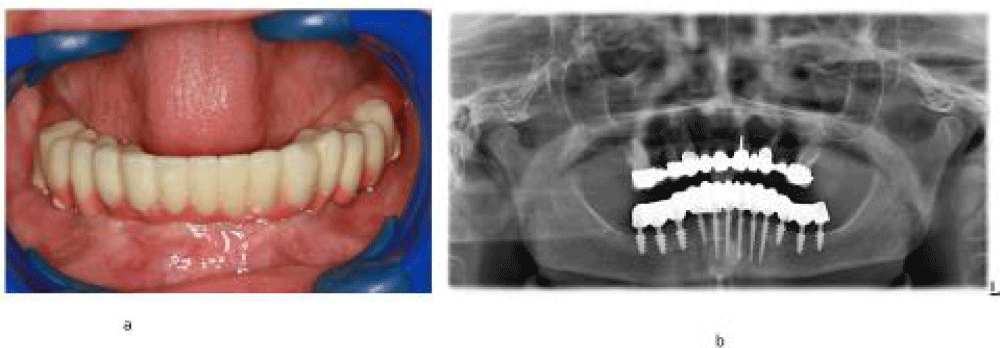
In the front region, implants of 14mm length and 3.5mm diameter were inserted flapless (Figure 3). After surgery, an impression was taken with transfer coping in place. A temporary bridge was fabricated on the chairside for the mandible and fixed with temporary cement.
Four days after the framework, a try-in was done and a new bite registration was taken. The smile line and aesthetic outlook were decided at this session. Five days after the try-in an appointment for prosthesis delivery was given. The bridge was fixed in the mandible with temporary cement (Figure 4). The patient was reviewed after 2 weeks. Thereafter, the patient was scheduled for follow-up at 3 months and then every 6 months.
Patient 2 is a 91-year-old patient with a full prosthesis who was not happy with her prosthesis and wanted fixed prosthesis in the mandible. Patient’s family was afraid of implant placement because of the age of the patient. At presentation patient was in good health, after clinical examination, the possibility of implants treatment was discussed. At the first appointment, panoramic radiograph was taken to check if there was enough bone for implant placement.
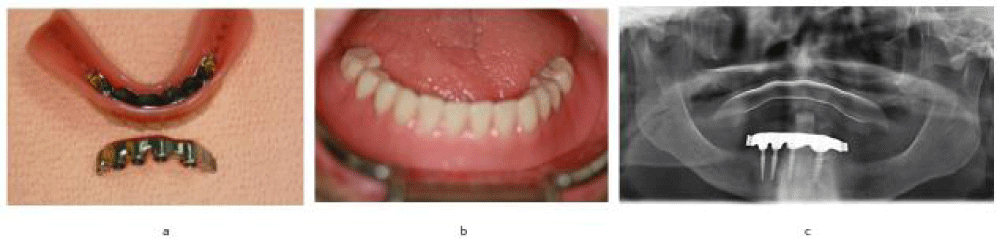
On the next appointment, one-piece implants of 3,5mm diameter and 14mm length (ROOTT implant system) were inserted flapless in positions 31, 32, 41 and 42 with a torque of 50N.
After the implant placement, a silicone impression was taken and bite registration was done.
At the third appointment, bar was cemented and the lower prosthesis was delivered (Figure 5).
Discussion
One-piece implants facilitate oral rehabilitation and accelerate tooth replacement procedure [9,14]. The implant permits minimally invasive surgical techniques with a simpler treatment sequence at lower costs [13].
When compared to conventional implants, one piece implants are cost-effective, they eliminate the need for cover screws, healing abutments, subsequent separate implant attachments or separate implant abutments [13,14].
In the above cases, one piece compressive implants (from ROOTT TRATE.AG) were used. These are single component implants with a compression thread. The special compressive thread produces compression when inserted into the cancellous bone, thereby creating a layer of cortical bone around the implant which allows immediate loading with high primary stability. The abutment direction on the implant can be adjusted up to 15° relative to the implant axis [15-18].
The compressive one piece implant can be used to restore single crowns and anterior cemented bridges, or multiple unit restorations with immediate loading in the upper and lower jaws with adequate bone tissue. It can also be used in combination with a conventional implant and it allows flap and flapless placement. The implants insertion is similar to that of crestal implants, with a recommended minimum torque of 35 N/cm.
All cases above were performed free hand by the second author (who designed the implant with the collaboration of the Swiss company TRATE) without any associated complications, however training and experience is needed in order to achieve a good result.
Flapless implant placement require training and experience as well as the recognition by the surgeon of the possible pitfalls of the technique. The knowledge of the available bone is important in a flapless procedure. An adequate amount of bone must be present for root form screw type implant to be placed.
Narrow diameter implants as seen in the case reports above may be placed flaplessly but a denser quality of bone may be necessary for implant stability as well as an adequate zone of attached gingiva for protection of the implant epithelial coronal attachment [19].
The presented case reports show the functional restoration of an edentulous patient with minimal invasive surgical technique with one piece implant in elderly patients. Rehabilitation of seemingly difficult edentulous cases was achieved within a short period of time.
References
- Ali SA, Karthigeyan S, Deivanai M, Kumar A. Implant rehabilitation for atrophic maxilla: a review. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014; 14: 196-207. https://goo.gl/MisV74
- Belser UC, Buser D, Hess D, Schmid B, Bernard JP, Lang NP. Aesthetic implant restorations in partially edentulous patients-a critical appraisal. Periodontol 2000. 1998; 17: 132-150. https://goo.gl/b4oowB
- Bidra AS. Three-dimensional esthetic analysis in treatment planning for implant-supported fixed prosthesis in the edentulous maxilla: review of the esthetics literature. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2011; 23: 219-236. https://goo.gl/npKoBJ
- Mericske-Stern RD, Taylor TD, Belser U. Management of the edentulous patient. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000; 11: 108-125. https://goo.gl/G2Wrjf
- Bosse LP, Taylor TD. Problems associated with implant rehabilitation of the edentulous maxilla. Dent Clin North Am. 1998; 42: 117-127. https://goo.gl/LHxC6V
- Candel E, Penarrocha D, Penarrocha M. Rehabilitation of the atrophic posterior maxilla with pterygoid implants: a review. J Oral Implantol. 2012; 38: 461-466. https://goo.gl/vphwci
- Candel-Marti E, Carrillo-Garcia C, Penarrocha-Oltra D, Penarrocha-Diago M. Rehabilitation of atrophic posterior maxilla with zygomatic implants: review. J Oral Implantol. 2012; 38: 653-657. https://goo.gl/q5aQiY
- Esposito M, Ardebili Y, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: different types of dental implants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; 7. https://goo.gl/PDGS9G
- Lauritano D, Grassi R, di SD, Lucchese A, Petruzzi M. Successful mandible rehabilitation of lower incisors with one-piece implants. J Med Case Rep. 2014; 8: 406-408. https://goo.gl/ijWSCi
- Markwardt J, Weber T, Modler N, Sembdner P, Lesche R, Schulz MC, et al. One vs. two piece customized implants to reconstruct mandibular continuity defects: a preliminary study in pig cadavers. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014; 42: 790-795. https://goo.gl/67ABaA
- Wu AY, Hsu JT, Chee W, Lin YT, Fuh LJ, Huang HL. Biomechanical evaluation of one-piece and two-piece small-diameter dental implants: In-vitro experimental and three-dimensional finite element analyses. J Formos Med Assoc. 2016; 115: 794-800. https://goo.gl/Mgz8bd
- Jung RE, Grohmann P, Sailer I, Steinhart YN, Fehér A, Hammerle C, et al. Evaluation of a one-piece ceramic implant used for single-tooth replacement and three-unit fixed partial dentures: a prospective cohort clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016; 27: 751-761. https://goo.gl/h3HQUp
- Rajput N, KPS, GR, SCC. Mohammed J. Minimally invasive transmucosal insertion and immediate provisonalization of one-piece implant in partially edentulous posterior mandible. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013; 7: 2070-2073. https://goo.gl/dWr1nj
- Wang QN, Li M, Qiu J, Zhang XZ, Wu ZQ, Chen DL, et al. Application of one-piece implant-supported detachable telescope retained fixed bridge in edentulous cases. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2015; 24: 702-707. https://goo.gl/3y9N4T
- Barrachina-Diez JM, Tashkandi E, Stampf S, Att W. Long-term outcome of one-piece implants. Part II: Prosthetic outcomes. A systematic literature review with meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013; 28: 1470-1482. https://goo.gl/PiHgfB
- Cannizzaro G, Leone M, Consolo U, Ferri V, Esposito M. Immediate functional loading of implants placed with flapless surgery versus conventional implants in partially edentulous patients: a 3-year randomized controlled clinical trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008; 23: 867-875. https://goo.gl/N4cA4a
- Fürhauser R, Mailath-Pokorny G, Haas R, Busenlechner D, Watzek G, Pommer B. Esthetics of flapless single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla using guided surgery: association of three-dimensional accuracy and pink esthetic score. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015; 17: 427-33. https://goo.gl/Xqu8Cy
- Pozzi A, Polizzi G, Moy PK. Guided surgery with tooth-supported templates for single missing teeth: a critical review. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016; 9: 135-153. https://goo.gl/GSWs7L
- Flanagan D. Flapless dental implant placement. J Oral Implantol. 2007; 33: 75-83. https://goo.gl/a7AhWd
Authors submit all Proposals and manuscripts via Electronic Form!